How to Optimize for Conversational Queries and Voice Search?
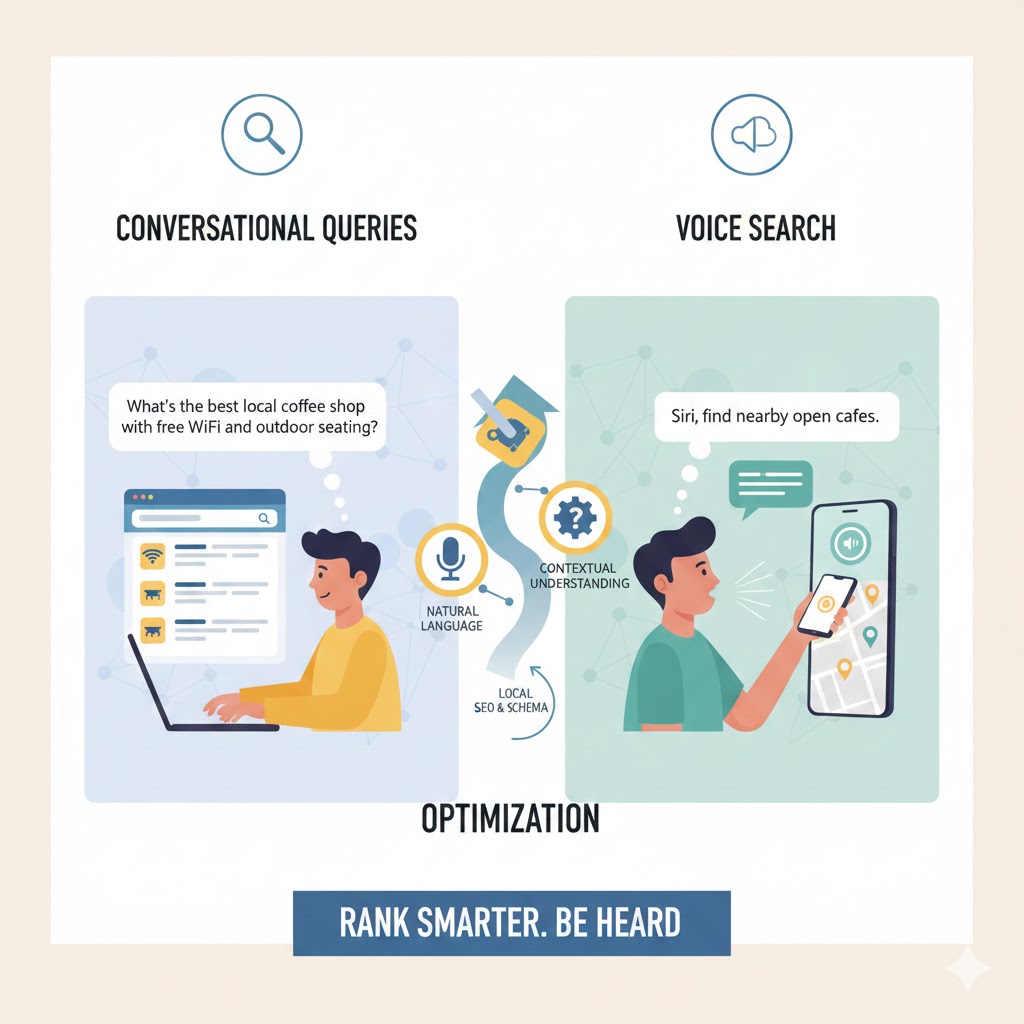
Every year, we watch search behavior shift again but few shifts have been as transformative as the rise of conversational queries and voice search. As users move from typing keywords to speaking naturally into phones, smart speakers, and AI assistants, businesses must rethink how they structure content and technical signals.
Today’s consumers don’t search like machines.
They search like humans.
And our websites must respond like humans too.
Whether someone is asking a question on a smart speaker, chatting with an AI assistant, or dictating a query on their phone, the goal remains the same:
Search engines want to deliver the most relevant, clearest, most answer-ready response.
In this guide, we break down exactly how we optimize for conversational queries, voice search, and the fast-growing universe of natural-language discovery.
Why Conversational Search Has Changed Everything?
Traditional search relied on short, clipped phrases like:
- “best dentist Chicago”
- “fix leaking pipe”
- “coffee shop near me”
Voice-driven and conversational search now sounds like:
- “Who’s the best dentist near me for weekend appointments?”
- “Why is my pipe leaking under the bathroom sink?”
- “What’s a good coffee shop nearby with Wi-Fi and outdoor seating?”
The difference isn’t just length, it’s intent, context, and natural language.
This shift pushes us to optimize content for how people actually talk, not how they used to type.
What Exactly Are Conversational Queries?
Conversational queries are questions, statements, and requests expressed in natural language. They reflect how people speak, not how they type.
These queries typically:
- Include full sentences
- Contain contextual clues
- Ask direct questions
- Express clear intent
- Mimic human conversation
This creates opportunities for brands willing to craft content that speaks back in the same style.
Why Voice Search Matters More Than Ever?
Voice search isn’t just a feature, it’s a behavior.
We now see it in:
- Smart speakers
- Mobile voice assistants
- In-car navigational systems
- AI chat models
- Smart TVs
- Wearable devices
As these devices multiply, spoken queries grow exponentially.
Optimizing for them helps us appear in:
- Zero-click answers
- Featured snippets
- AI assistant recommendations
- Local “near me” results
- Voice-led shopping and service requests
Our goal is to speak the user’s language, literally.
How We Adapt Our Content Strategy for Natural Language?
To perform well in conversational search, our content must provide:
- Clear answers
- Natural phrasing
- Conversational tone
- Q/A-oriented structure
- Short paragraphs
- Intent-aligned headings
Search engines translate speech into text and then search for answers that match tone, clarity, and structure.
When our content mirrors spoken patterns, engines surface us more often.
Step 1: Identify Conversational Intent Before Writing
Conversational queries fall into a few natural patterns:
1. Question-Based Queries
Examples include:
- “How do I…?”
- “Where can I…?”
- “Who’s the best…?”
- “Why does…?”
2. Descriptive Queries
“What’s the fastest way to…”
“What do I need to…”
3. Problem-Focused Queries
“My AC isn’t cooling, what do I do?”
4. Localized Queries
“Where can I get my car fixed near me?”
We listen to the language our customers use and build content that reflects it directly.
Step 2: Structure Content Using Natural Questions
We weave questions into headings, intros, and transitions.
This aligns with AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), a must for voice search.
Examples we use:
- “How can we optimize a page for voice search?”
- “What makes conversational queries different from typed ones?”
- “Why do smart assistants choose one answer over another?”
This structure helps both people and AI find what they need instantly.
Step 3: Create Short, Direct, Answer-Ready Content
For spoken responses, search engines want:
- 2–3 sentence answers
- Clear definitions
- Immediate context
- Streamlined explanations
If a user asks:
“How do I optimize my website for voice search?”
We want to answer quickly:
“Optimize your content for natural questions, add structured data, improve mobile speed, and provide clear, concise answers that AI assistants can read easily.”
Short. Clear. Actionable.
Step 4: Use Long-Tail, Conversational Keywords Naturally
We integrate long-tail phrases that mirror human speech:
- “How do I find the best plumber near me?”
- “What’s the easiest way to fix a slow computer?”
- “Where can I get affordable landscaping in my area?”
We avoid stuffing.
We simply write the way people talk.
Step 5: Strengthen Local Voice Search Signals
Most voice queries carry local intent.
Examples:
- “pizza near me”
- “closest urgent care open now”
- “best realtor in my neighborhood”
To win voice+local, we optimize:
- NAP consistency
- Google Business Profile
- Local pages
- Service-area descriptions
- Schema for location
- Conversational local content
We also naturally mention local details in our writing to support GEO optimization.
Step 6: Use Schema Markup to Boost Answer Visibility
Voice search relies heavily on structured data.
We add:
- FAQ schema
- HowTo schema
- LocalBusiness schema
- Service schema
- Article schema
Schema helps AI understand who we are, what we offer, and why our answer is relevant.
Step 7: Prioritize Speed and Mobile Optimization
Most voice searches happen on mobile.
If our site loads slowly or renders poorly, AI assistants choose another source.
We prioritize:
- Lightweight pages
- Mobile-first design
- Clean code
- Fast servers
- Core Web Vitals
Fast, accessible pages win.
Step 8: Write in a Voice-Friendly Tone
Voice queries expect voice-friendly answers.
We prioritize:
- Conversational tone
- Short sentences
- Easy-to-read language
- Clear transitions
- Natural flow
The easier our writing is to read aloud, the easier it is for AI to choose it.
Step 9: Build Topic Clusters Around Common Questions
We build clusters such as:
- “How to Improve Voice Search Visibility”
- “Local Voice Search Strategies”
- “Optimizing for AI and Conversational Engines”
- “Conversational Content Writing Tips”
Clusters improve topical authority essential for voice-driven results.
Step 10: Continuously Monitor Search Behavior Shifts
Conversational trends shift quickly.
We track:
- Voice query patterns
- Local answer behaviors
- Zero-click appearances
- Popular long-tail questions
- Shifts in generative responses
This lets us adjust content proactively.
We don’t wait for ranking drops, we evolve continually.
How We Use AI Tools to Improve Conversational Optimization?
We use AI to:
- Extract real user questions
- Analyze natural speech patterns
- Identify new conversational keywords
- Map question clusters
- Predict trending voice queries
But we always add human refinement to maintain tone, relevance, and accuracy.
A Practical Voice Search Transformation
A service provider approached us struggling to appear in voice-based queries despite strong SEO.
The Problem:
Their content lacked question-based structure, natural phrasing, and schema clarity.
Our Solution:
We rebuilt key pages with:
- Headings written as natural questions
- Clear 2–3 sentence answers
- Local conversational signals
- FAQ schema
- Improved internal linking
Within months, they began appearing in more voice-led searches, especially for “near me” and long-tail conversational queries.
FAQs
These questions appear naturally in the flow, not as a separate FAQ page:
- How do conversational queries differ from typed searches?
- What makes content voice-search-friendly?
- How does schema help AI assistants choose an answer?
- How can local businesses optimize for spoken “near me” queries?
Why Conversational Optimization Is the Future?
As search becomes more human, so must our content.
Optimizing for conversational queries and voice search isn’t just a strategy, it’s becoming the foundation of how users find information in a world shaped by AI, speech, and natural language.
When we match the way humans talk, we match the way AI understands.
And when we provide clear, structured, natural answers, we become the brand that gets chosen, in text, voice, and everywhere users search.